WHITE PAPER
MRO ORCHESTRATION 2026: How Connected Workflows Reduce TAT VariabilityDecember 2025
Key Takeaways:
- Predictability matters more than speed, as reducing TAT variability improves planning confidence and fleet availability.
- Most delays are invisible and avoidable, driven by disconnected systems, manual handoffs, and supply chain blind spots rather than maintenance work itself.
- Orchestration synchronizes MRO execution, connecting people, parts, tools, data, and decisions so work continues despite disruptions.
- Connected workflows tighten TAT performance, reducing outliers and enabling more reliable delivery and customer commitments.
- Significant gains are achieved without added capacity, as orchestration eliminates idle time and can reduce turnaround duration by up to one-third.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Predictable Maintenance in an Unpredictable World
Aviation, aerospace, and defense organizations are under increasing pressure to deliver predictable, reliable, and efficient maintenance outcomes. Aging aircraft fleets, constrained shop capacity, technician shortages, and fragmented MRO systems have created significant variability in turnaround times (TAT).
This whitepaper explores how MRO orchestration, supported by connected workflows, digital thread alignment, real-time asset tracking, and modern aircraft MRO software platforms, reduces TAT variability and strengthens fleet readiness. Building on earlier insights from maintenance performance, workforce management, and digital transformation, this paper demonstrates why orchestration is the essential next step for aviation and aerospace MRO excellence.
Rather than optimizing for speed alone, orchestration optimizes for predictability, consistency, and synchronized execution. When delays are visible, connected, and proactively resolved, maintenance organizations achieve tighter turnaround windows, improved planning confidence, and higher operational efficiency.
The Aviation and Aerospace MRO Landscape Today
Aviation and aerospace maintenance organizations are experiencing unprecedented operational complexity. Commercial, business, and defense aircraft are remaining in service longer, while MRO facilities, skilled labor availability, and supply chain throughput have not kept pace with rising demand.
As utilization increases, so does the pressure on MRO management teams to deliver predictable maintenance outcomes. Many aviation MRO facilities operate at or beyond capacity, causing even minor delays to ripple across fleets, schedules, and customer commitments.
Industry leaders now recognize that average TAT is no longer the primary performance indicator. Instead, the variability between the fastest and slowest outcomes is what disrupts fleets, increases costs, and reduces customer confidence.
A heavy maintenance check performed in one facility may finish 20–40 percent faster than in another, even under similar conditions. This inconsistency forces airlines and operators to increase spare aircraft coverage, inflate schedule buffers, and plan conservatively — all of which reduce operational flexibility.
Predictability has become more valuable than pure speed.
Root Causes of TAT Variability
Most TAT variability comes not from the tasks themselves, but from the hidden delays that occur between tasks. These friction points include:
- Fragmented MRO systems and disconnected data
Many organizations use a combination of legacy tools, standalone applications, spreadsheets, paper travelers, and partially integrated aircraft MRO software.When planning, engineering, supply chain, and execution systems do not share real-time data — or the digital thread is broken — delays remain invisible until they become bottlenecks. - Supply chain unpredictability and MRO inventory blind spots
Parts may be available but not staged correctly. Or they may be expected but delayed. This is often caused by gaps in asset tracking, MRO inventory visibility, and maintenance-aware supply chain planning. - Manual coordination between shifts and departments
When teams rely on emails, calls, or ad-hoc communication, inconsistencies arise between shifts, bays, and sites. - Engineering disposition delays
Awaiting engineering review or manual approvals can stall work without any visibility into downstream impact. - Workforce variation
Differences in technician experience, training, access to digital decision support tools, or process interpretation cause measurable variation across tasks and shifts.
Even organizations with digitized documentation still experience fragmentation. Digital tools alone are not enough. Without orchestration, delays remain invisible, unpredictable, and unpreventable.
What MRO Orchestration Means
MRO Orchestration is the end-to-end synchronization of maintenance activities across people, parts, tools, data, and decisions. It is not simply system integration or the digitization of paper. It is the creation of a connected MRO platform that ensures work flows continuously with minimal disruption.
In traditional aviation maintenance environments, work is executed sequentially. When a task stalls because of a missing part, engineering disposition, approval, or tool, everything downstream stalls as well. Orchestration changes that.
With orchestration:
- Dependencies are visible.
- Delays are detected early.
- Parallel tasks are elevated to keep momentum.
- Technicians and planners receive real-time insights and guidance.
- Supply chain becomes maintenance-aware instead of reactive.
This approach transforms aviation and aerospace maintenance operations, enabling:
- Reduced TAT
- Higher technician productivity
- Lower variability in outcomes
- Improved fleet availability
- Stronger customer confidence
Real-world examples show that orchestration without adding labor or equipment can reduce turnaround duration by nearly one third, simply by removing the invisible waiting periods between tasks.

Image 1
The Six Pillars of MRO Orchestration
Impresa’s orchestration model is built on six foundational pillars that support next-generation aviation and aerospace MRO solutions, MRO ERP capabilities, and connected digital thread ecosystems.
- Connected Asset and Operational Data
Technicians, planners, engineers, and leadership must all access the same real-time information. When aircraft histories, manuals, job cards, and digital thread data are unified in a single MRO platform, decisions accelerate and rework decreases.
- Orchestrated Task Execution
Tasks are sequenced dynamically based on dependency, availability, and readiness — not rigid linear order. If one task is blocked, others are automatically elevated to maintain flow.
This ensures maximum forward progress and eliminates idle time.
- Prediction-to-Execution Alignment
Forecasting and execution must be linked. This includes:
- Pre-staged materials
- Anticipated labor demand
- Optimized shop capacity
- Maintenance-aware supply chain planning
This connection dramatically improves schedule reliability.
- Maintenance-Aware Supply Chain
The supply chain shifts from reactive to proactive when it is directly tied to maintenance plans.
This improves MRO inventory management, reduces stockouts, and ensures the right part arrives at the right time — not after a delay has already occurred.
- Workforce Augmentation and Digital Guidance
Digital work instructions, AI assistants, mobile tools, and contextual knowledge access reduce variation between technicians and shifts.
This is especially valuable for aerospace and defense environments where compliance, traceability, and precision are mandatory.
- Integrated Fleet-to-Component Planning
Local decisions must align with system-wide constraints. Orchestration ensures that component repairs, heavy checks, and line maintenance all support broader fleet readiness targets.
This reduces conflict, eliminates scheduling surprises, and strengthens operational coordination.
Quantifying the Impact of MRO Orchestration
One of the most effective ways to measure orchestration impact is through distribution curves of turnaround times.
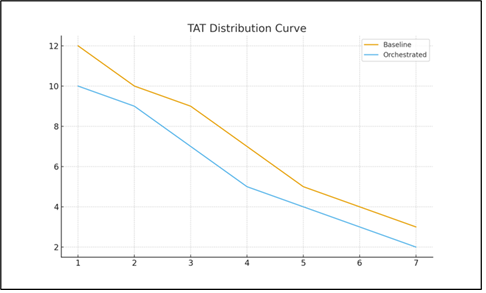
Figure 2: Baseline vs. Orchestrated Turnaround Times
Without orchestration:
- TAT is highly variable
- Outliers dominate planning
- Schedules require buffer time
- Spare aircraft requirements increase
With orchestration:
- The curve tightens
- Variability decreases
- Schedules become predictable
- Customer commitments improve
- Fleet availability increases
Real Results
Organizations implementing orchestration have achieved:
| Metric | Improvement |
| On-Time Delivery | 15% |
| TAT Reduction | 33% |
| Cost Avoidance | 20% |
Return on investment comes from dozens of small improvements: fewer pauses, faster engineering approvals, proactive staging, and reduced rework. These gains accumulate, producing measurable and sustained operational value.
Implementation Roadmap to 2026
Orchestration is a scalable journey, not a single deployment. Impresa recommends a four-phase roadmap for aviation and aerospace organizations.
Phase 1 — Assessment and Fragmentation Mapping
Identify delays, manual handoffs, disconnected systems, and digital thread breaks.
A readiness checklist establishes current-state maturity.
Phase 2 — Prioritize High-Impact Workflows
Select areas with the highest variability or greatest operational value.
Early wins accelerate organizational adoption.
Phase 3 — Deploy the Orchestration Platform
Implement orchestration across people, processes, and technology.
Key elements include:
- KPI dashboards
- Real-time data visibility
- Automated workflows
- Technician guidance
- Maintenance-aware supply chain integration
Phase 4 — Scale and Continuously Improve
Establish governance, monitor reliability metrics, and expand orchestration across the enterprise. Cross-site alignment and change management are essential for sustained impact.
Readiness and Action
Aviation, aerospace, and defense MRO organizations ready to begin orchestration should:
- Conduct a variability assessment
- Map digital thread gaps
- Evaluate real-time visibility needs
- Identify manual bottlenecks
- Choose pilot workflows
- Define measurable outcomes
The urgency is clear: fleets are aging, demand is rising, and capacity is tightening. Organizations that implement orchestration now will gain a long-term competitive advantage in predictability, throughput, and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Orchestration represents the next frontier in aviation, aerospace, and defense maintenance excellence. While digital tools have improved visibility and documentation, true transformation occurs only when workflows flow continuously across people, parts, tools, files, and data.
Organizations that adopt connected MRO platforms, digital thread alignment, advanced asset tracking, and coordinated workflows will achieve predictable outcomes, stronger fleet readiness, and higher operational confidence.
The future belongs to MRO organizations that can deliver consistent, reliable, orchestrated execution.
References
- Oliver Wyman. (2025). Global Fleet & MRO Market Forecast 2025–2035.
Retrieved from: https://www.oliverwyman.com/our-expertise/insights/2025/feb/global-fleet-and-mro-market-forecast-2025-2035.html - Grand View Research. (2024). Aircraft MRO Market Size, Share & Industry Growth Report, 2030.
Retrieved from: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/aircraft-mro-market - International Air Transport Association (IATA). (2025). The Global Commercial Aircraft Fleet.
Retrieved from: https://www.iata.org/en/publications/economics/reports/the-global-commercial-aircraft-fleet/ - McKinsey & Company. (2024). What Does the Future Hold for Commercial Aviation Maintenance?
Retrieved from: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/aerospace-and-defense/our-insights/what-does-the-future-hold-for-commercial-aviation-maintenance - com. (2025). Aircraft MRO Industry Report, 2025-2034 (Summary).
Retrieved from: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/aircraft-mro-industry-report-2025-101800586.html - Aircraft Repair and Maintenance Industry Association (ARSA). (2025). Worldwide Civil Aviation Maintenance Industry Assessment.
Retrieved from: https://arsa.org/market-assessment/
© 2025 Impresa Corp. All rights reserved.
This whitepaper and its contents are the intellectual property of Impresa Corp. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means—electronic mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise—without the prior written permission of the publisher, except in the case of brief quotations used in critical reviews or scholarly works.
Impresa Corp. retains all rights to the methodologies, case studies, and concepts presented herein. For permissions or licensing inquiries, please contact info@impresa-us.com
Disclaimer: The information provided in this whitepaper is for general informational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the content, Impresa Corp. makes no warranties, express or implied, and assumes no legal liability for the use of this information. Readers are encouraged to seek professional guidance specific to their operational or regulatory requirements.
